The Spiking Neural Processor T1 is Innatera's ultra-low-power neuromorphic microcontroller SoC for real-time intelligence close to the sensor. It integrates a spiking neural network accelerator, a convolutional neural network accelerator and a RISCV core. T1 targets applications in battery-powered, power-limited and latency-critical devices.
Developed By:
Overview
The Spiking Neural Processor (SNP) T1 is a neuromorphic chip produced by Innatera, a semiconductor company based in Delft, Netherlands. The SNP is positioned as a single-chip solution for always-on sensing applications where tight constraints on power, latency, and cost are critical. Example applications include hearables/wearables, smart-home and other battery-powered IoT and edge devices.
- Power consumption in sub-mW or mW range
- Millisecond latency for real-time inference
- SNNs, CNNs, and CPU on one SoC
- Diverse interfaces: QSPI, I2C, UART, JTAG, GPIO, front end ADC
- Tiny form-factor: 2.16mm x 3mm, 35-pin WLCSP package
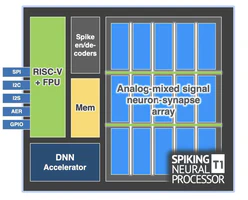
Architecture
The SNP T1 is designed to be the only SoC a sensor needs to be interfaced with and comes with a CPU and general purpose I/O included. The mixed-signal core of the SNP is a programmable multi-core pseudo-crossbar array of spiking neurons and synapses that can be configured into parallel and customizable neural network topologies. This array provides the capability to accelerate spiking neural networks (SNNs). SNNs differ from traditional neural networks in that their inputs and outputs are binary spike events over time rather than continuous values.
In addition to the SNN accelerator, T1 also includes a CNN accelerator and a 32-bit RISCV core with 384 KB of memory for more conventional workloads.
Interfacing
The SNP contains front-end interfaces to connect various sensors such as radar, microphones, and physiological sensors through standard digital interfaces or using direct analog interfacing using the included front-end ADC.
Software
To program the SNP, Innatera provides an SDK called Talamo that uses the PyTorch deep learning framework. This allows developers to build and train SNN models without needing specialized knowledge of neuromorphic hardware or SNN expertise. Talamo includes a model/topology zoo as well as reference implementations to allow non-SNN experts to quickly run models on the platform. A compiler, simulator, and integration into MLOps tooling are also available.
Help Us Improve this Guide
Our hardware guide is community-maintained. If you know of a chip we should add, see an error, or have updated information, please let us know by opening an issue on our GitHub repository.